You may already know a lot about the benefits of the ketogenic diet. However, this diet can be harmful to your health if you don’t know one important piece of information. You see it as a healthy diet and choose to stick to it for the rest of your life, but this can come with serious risks.
Why the Ketogenic Diet Helps You Lose Weight Faster
The ketogenic diet is considered a very effective way to lose weight in the short term. The ketogenic diet differs from the typical diet in that it has two main features: high fat and very low carbs.
The percentage of dietary calories on the keto diet is approximately 70-80% fat, 5-10% carbohydrates, and 10-20% protein. In some cases, the ketogenic diet’s lipids may even provide 90% of his daily calories.
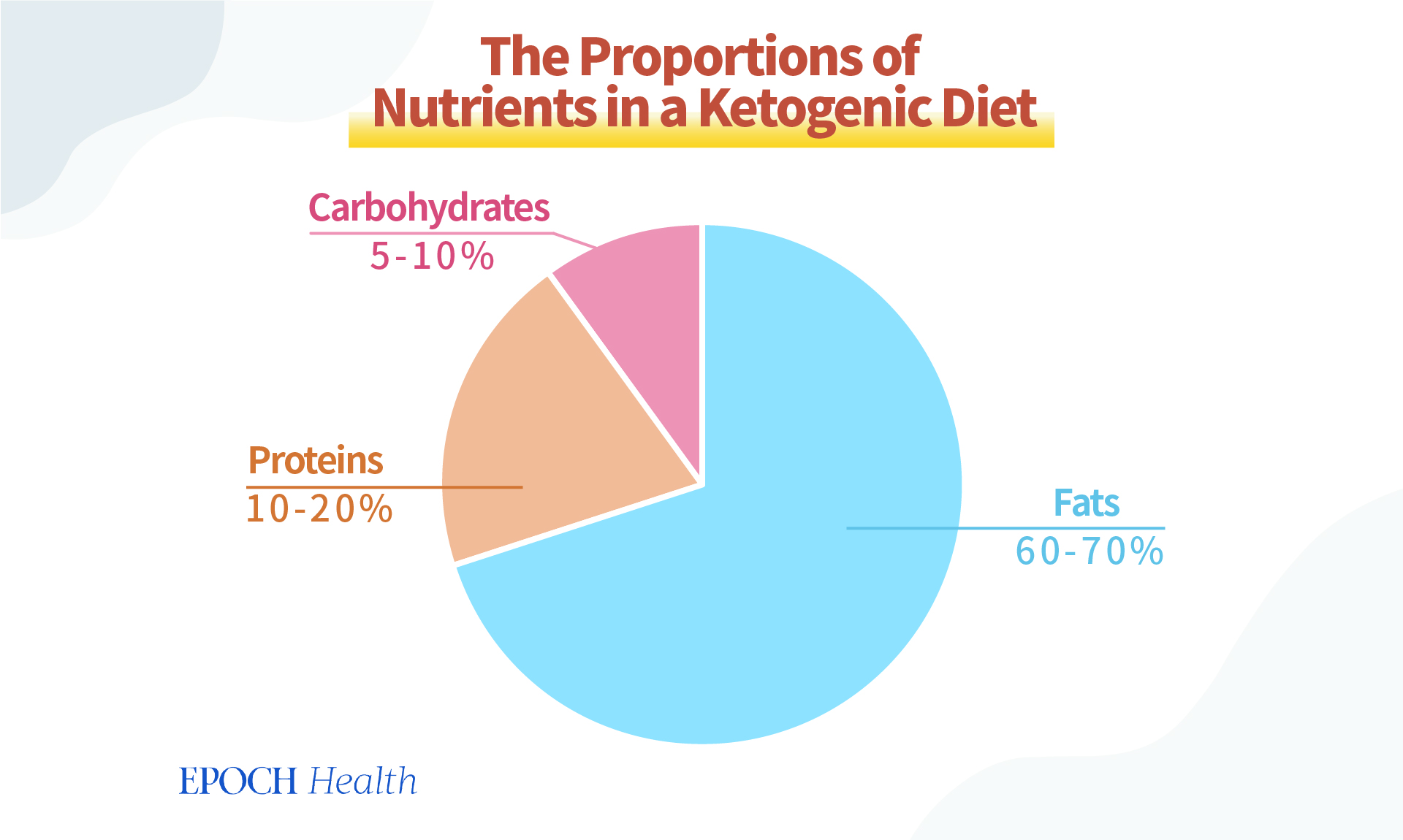
Assuming a standard dietary intake of 2,000 kcal per day, a ketogenic diet should consume between 20 and 50 grams of carbohydrates and not exceed 50 grams. To do. As you may know, a medium sized banana has 27 grams of carbs.
When carbohydrate intake is restricted to less than 50 grams daily, insulin secretion is greatly reduced. When carbohydrate availability is low and glycogen stores are depleted, the body is forced into certain metabolic changes such as ‘gluconeogenesis’ and ‘ketosis’.
Gluconeogenesis is the endogenous production of glucose and this process occurs primarily in the liver. The liver uses other substances such as lactic acid, glycerol and amino acids to make glucose.
When endogenous glucose is also unable to meet the body’s energy needs, the body begins using fat to produce ketone bodies to replace glucose as the body’s energy source.
During ketosis, blood sugar levels are relatively low and less insulin is secreted. This corresponds to decreased glucose storage and decreased fat production. At the same time, other hormonal changes can stimulate the breakdown of fats, converting them into ketone bodies that accumulate in the body.This metabolic state is called nutritional ketosis. In states of nutritional ketosis, the energy needs of organs and tissues are met primarily by ketones and fatty acids. Nutritional ketosis is considered relatively safe for a period of time.
Ketone bodies, also known as “superfuels,” produce more energy, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), compared to glucose. This allows the body to efficiently generate energy even in a calorie deficit. Ketone bodies can provide energy to the heart, muscle tissue, and kidneys. It can also cross the blood-brain barrier and provide alternative energy to the brain.
A sustained state of nutritional ketosis can help you lose even more weight because hunger subsides and overall caloric intake is reduced. One advantage is that you can maintain your basal metabolism without consuming too much muscle.
In addition to being an excellent source of energy for the body, ketone bodies have been shown in experiments to reduce free radical damage, increase endogenous antioxidant capacity, reduce inflammation, and have a positive impact on longevity and health. It is also proven.
The 6-12 months keto diet is very effective and good for your health
The ketogenic diet has received increasing attention and admiration in recent years. In addition to effective weight loss in the short term, it has also been shown to improve a range of human indicators, such as reducing blood lipids in the short term.
The optimal duration of the ketogenic diet is about 6-12 months. After this period, especially after he is two years old, the positive effects of the diet are no longer evident.
A general review published in Obesity Review conducted a global study of low-carbohydrate diets. We found that the metrics related to
Between 6 and 11 months, direct indicators of weight loss such as waist circumference, weight, and fasting blood sugar continued to decline. The sedative and regulatory effects of the diet on blood pressure were also attenuated.
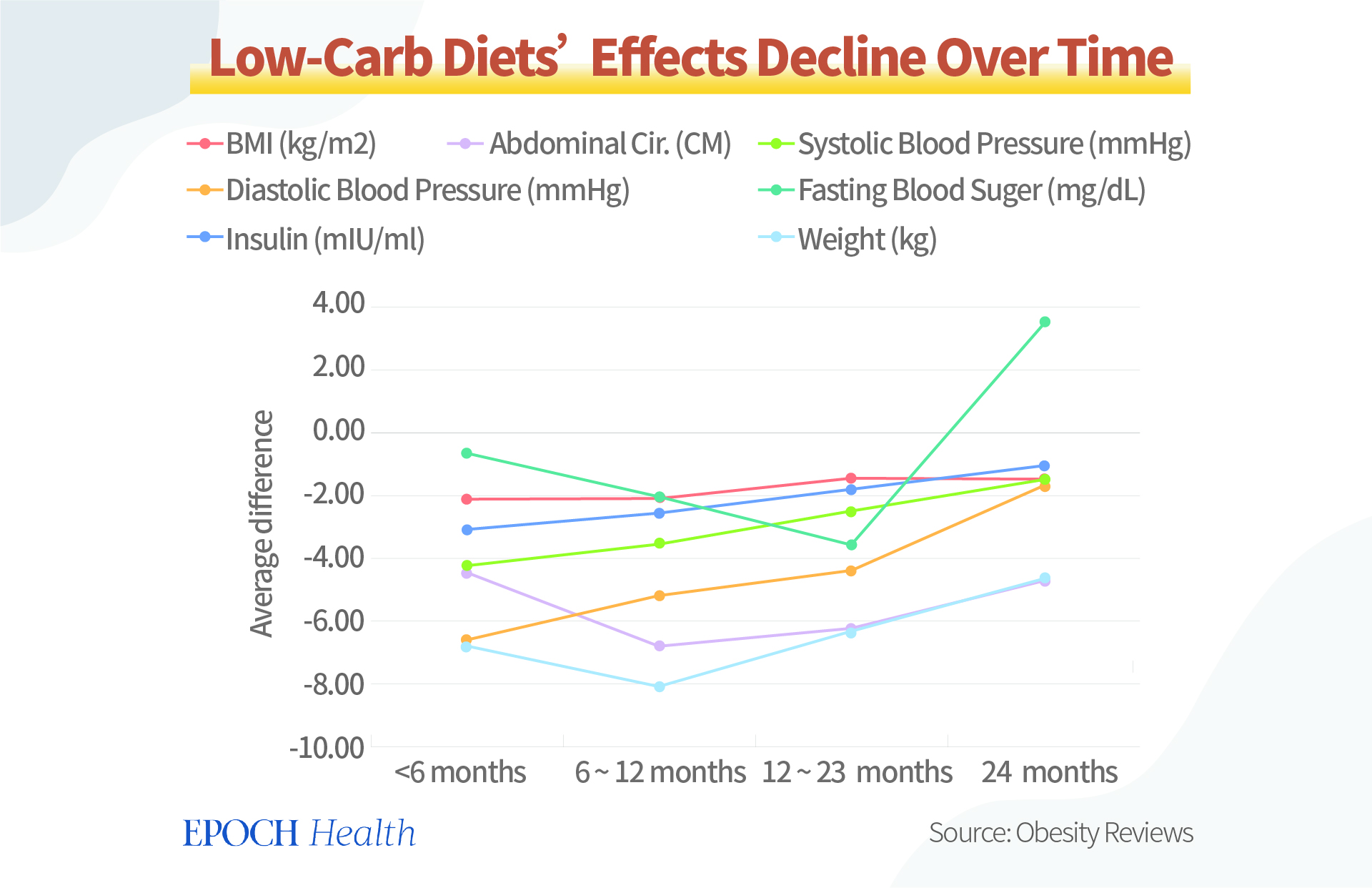
Entering the 12-23 month period, except for the fasting glycemic index, which was still declining, most other indicators stopped declining and began to rise further. By 24 months, many indicators were close to zero change and the fasting glycemic index was even higher.
Institutions such as the University of Florida are further researching the health effects of the length of the ketogenic diet.
The study found that decreases in blood pressure, triglycerides, glycosylated hemoglobin, increases in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (good cholesterol), and weight loss may be observed during the first 6-12 months. understood.
However, after 12 months on the ketogenic diet, these effects usually disappeared.
Increased blood lipids after more than a year on the keto diet
A ketogenic diet allows for healthy unsaturated fats such as nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds, avocados, tofu, and olive oil. A high intake of saturated fats is also recommended.
Long-term adherence to a ketogenic diet compared to a low-fat diet can lead to abnormal health indicators such as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. This is an increase in blood lipids that can lead to the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
Researchers conducted 12 relatively compelling experiments comparing low-fat and ketogenic diets in 1,258 participants. All experiments were over 12 months in duration. Results showed that following a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet for up to one year resulted in significantly higher blood lipids than a calorie-restricted, low-fat diet.
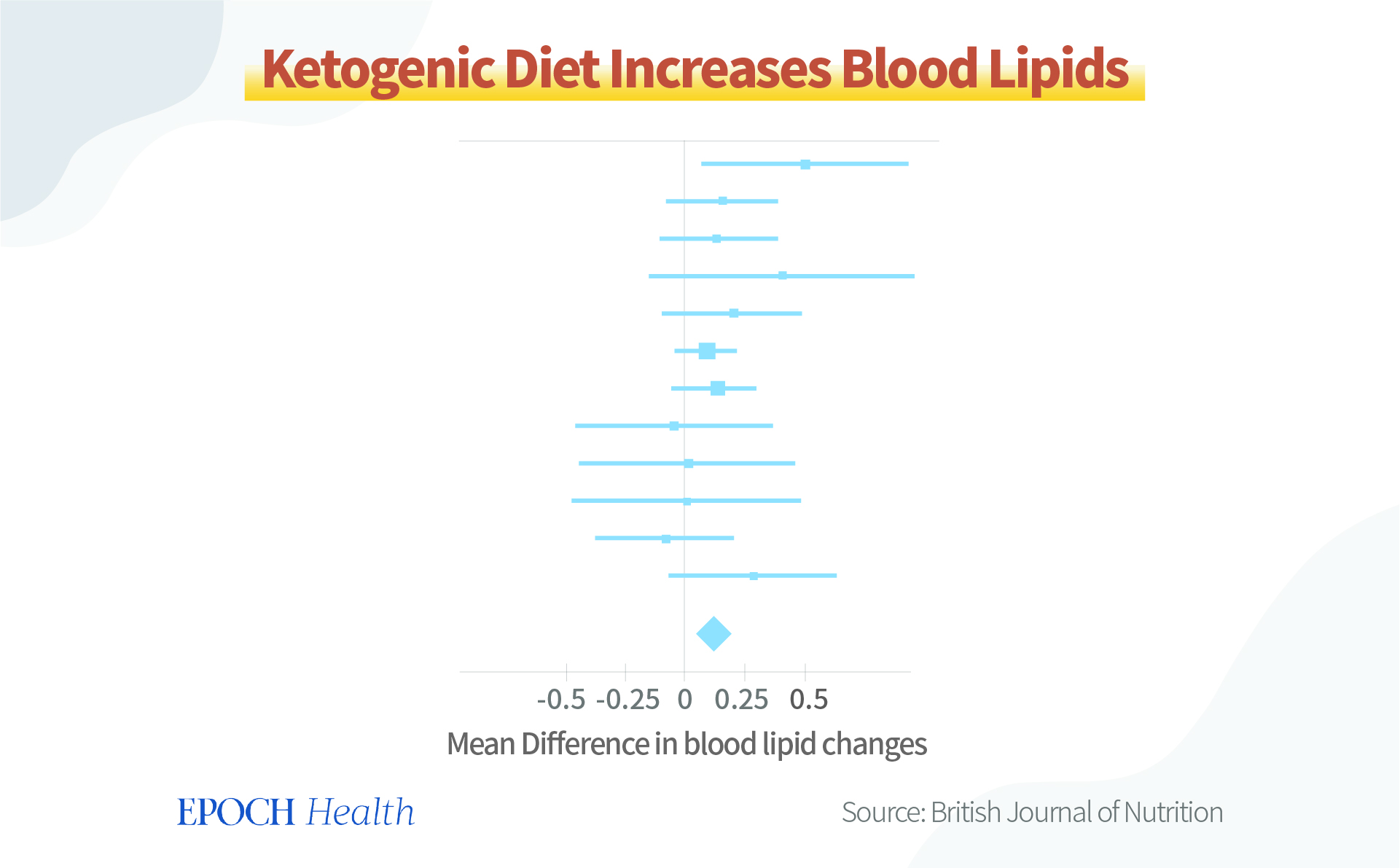
At the very least, the ketogenic diet has relatively little regulatory effect on blood lipids and may even increase blood lipids.
Additionally, some people cannot control their carbohydrate intake to 5-10% when following a ketogenic diet. The intake remains the same, but at relatively low levels. The problem with this diet is elevated blood lipids.
For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that people who ate a low-carbohydrate diet (30% carbohydrate, fat, and protein ratio), compared to those who ate a low-fat diet, 45 and 23 percent, respectively) had significantly elevated blood lipids. People in the low-fat diet group (carbohydrate, fat, and protein percentages were 48, 29, and 21 percent, respectively) did not have this problem and had reduced blood lipids.
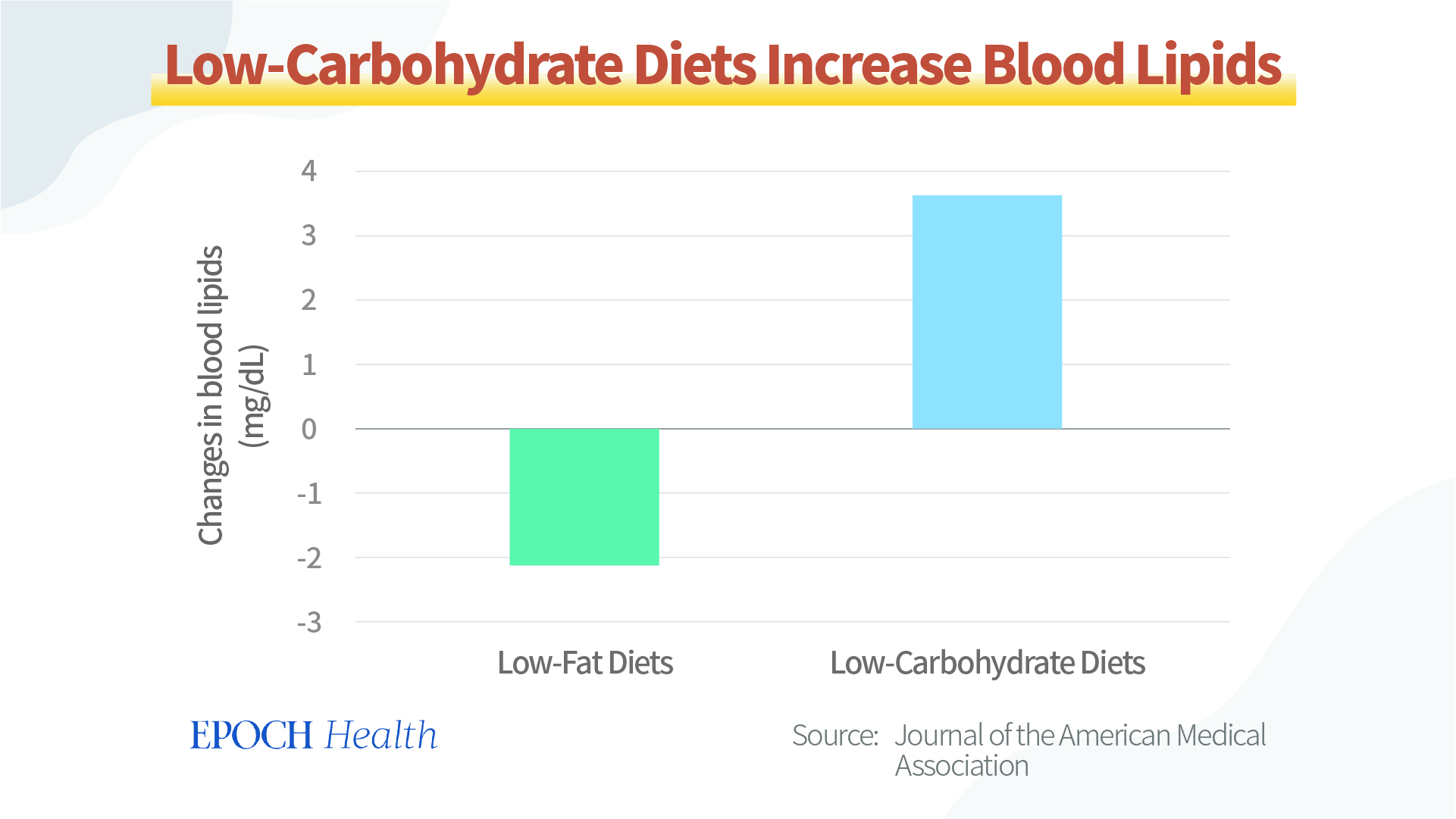
Scientists explain that “unintentionally” because low carbohydrate intake inhibits insulin production, which inhibits the action of some enzymes while stimulating the production of others. It can raise blood lipids and promote atherosclerosis.
Extended keto can lead to anemia and reduced antioxidant capacity
Currently, there are few conclusions about the long-term effects of the ketogenic diet on the human body. , and can lead to decreased antioxidant levels.
The study found that several physical indicators worsened in rats following the keto diet for 60 consecutive days, with 60 days in adult laboratory rats equivalent to 4 years in humans.
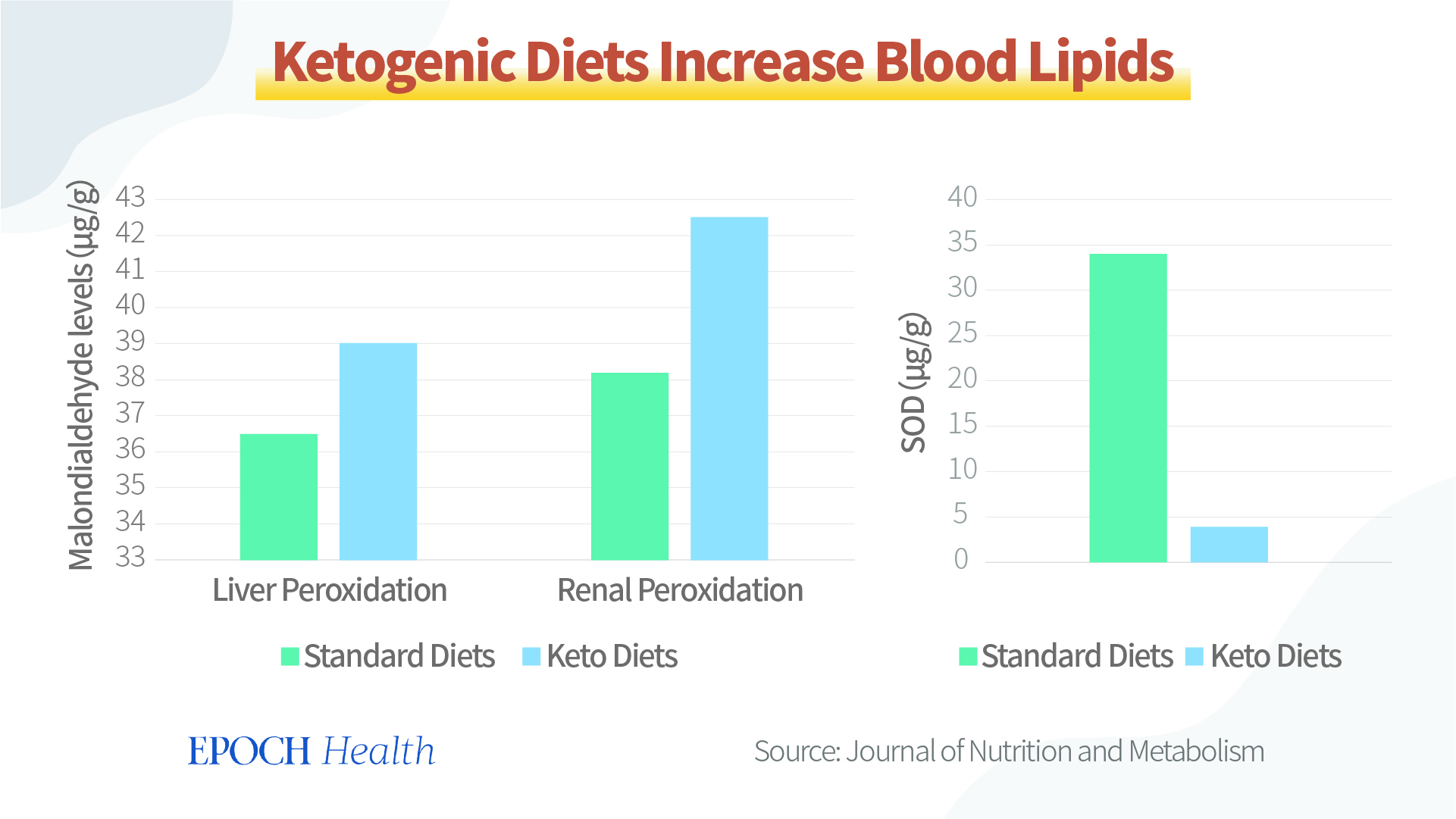
Among them, one characteristic change is that the ketogenic diet increases ketone bodies in the blood of rats. The pH value of the blood drops and acidosis develops. In addition, rats developed anemia with greatly reduced red blood cell and hemoglobin counts.
Long-term ketogenic diets also exacerbated hepatic and renal lipid peroxidation. At the same time, superoxide dismutase (SOD), a substance that represents antioxidant levels in the blood, is reduced.
The worst of the best diets?Other side effects of long-term ketosis
“US News & World Report” invited a number of experts to evaluate the world’s top 40 diets. The ketogenic diet ranks him 4th in the category of best diets for rapid weight loss, while he ranks 19th in the best diets for weight loss category. And it ranks 35th in both the best heart-healthy diet and easiest diet categories. And in the best diets for health category, the ketogenic diet actually ranks lowest.
Because the ketogenic diet severely limits carbohydrate intake, many vegetables, fruits, and grains are removed from the menu. There is a possibility
Limited grains and legumes are rich in fiber. Losing these sources of fiber not only increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, but it also affects bowel function and can lead to constipation.
The human brain needs sugar from healthy carbohydrates to function well, and a low-carbohydrate diet can cause hypersensitivity.
Additionally, long-term side effects of the ketogenic diet include fatty liver, kidney stones, hypoproteinemia, and vitamin deficiencies.
Remember to check how you feel about your diet plan.
.
