Overview: The study shows that doing household chores, exercise, and social interactions significantly reduces the risk of dementia.
sauce: AAN
Physical and mental activities such as housework, exercise, and visits with family and friends may help reduce the risk of dementia, according to a new study published on July 27, 2022. Neurology..
This study examined the effects of these activities, as well as mental activity and the use of electronic devices, in both people at high and low genetic risk for dementia.
“Many studies have identified potential risk factors for dementia, but I wanted to know more about different lifestyles and their potential role in the prevention of dementia,” said Sichuan, Chengdu. University research authors Huan Song, MD, PhD said. , China. “Our study found that exercise, household chores, and social visits were associated with a reduced risk of various types of dementia.”
The study enrolled 501,376 people from a dementia-free UK database with an average age of 56 years.
Participants completed a questionnaire at the beginning of the study, including those related to physical activity. I was asked how often I participated in activities such as climbing stairs, walking, and participating in intense sports. They were also asked what kind of transportation they used, such as housework, work-related activities, and commuting on foot or by bicycle.
Participants completed another questionnaire on mental activity. Whether to attend adult education classes, how often you visit with friends and family, how often you visit pubs, social clubs and religious groups, electronic devices such as playing computer games, watching TV, watching TV, etc. I was asked about the level of education about how often I use. Speak on the phone.
In addition, participants reported whether they had close relatives with dementia. This helped researchers determine if they were at genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Study participants were followed for an average of 11 years. At the end of the study, 5,185 people developed dementia.
After adjusting for multiple factors such as age, income, and smoking, researchers found that most of the physical and mental activity studied was associated with a risk of dementia. Importantly, the findings remain after considering the high correlations and interactions of these activities.
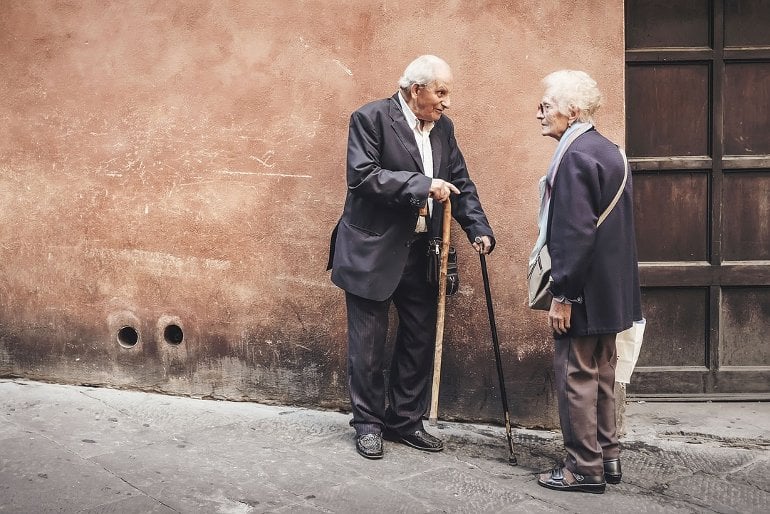

People who are highly engaged in activity patterns such as frequent exercise, household chores, and daily visits to family and friends are at 35% risk of dementia each compared to those who are least engaged in these activities. , 21%, and 15% lower. pattern.
Researchers also examined the incidence of dementia by identified activity patterns. The proportion of people who exercised frequently was 0.45 every 1,000 person-years, compared to 1.59 for those who did little exercise. The man-year takes into account the number of people who participated in the survey and the time spent on the survey.
The number of people who do household chores frequently was 0.86 per 1,000 person-years, compared to 1.02 for those who rarely do household chores.
The percentage of people who visited their families daily was 0.62 every 1,000 people a year, compared to 0.8 who visited their friends and family only once every few months.
See also
“Our study found that by engaging more often in healthy physical and mental activity, people can reduce their risk of dementia,” Song said. “We need more research to see our findings, but our results encourage that making these simple lifestyle changes can be beneficial. increase.”
Researchers have found that all participants, with or without a family history of dementia, benefit from the protective effects of physical and mental activity.
The limitation of the study was that people reported their physical and mental activities and may not remember or report these activities correctly.
Funds: This study was supported by the National Foundation for Natural Sciences of China, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, and the National Center for Clinical Research for Geriatrics.
About this dementia research news
author: Natalie Conrad
sauce: AAN
contact: Natalie Conrad – AAN
image: The image is in the public domain
Independent research: The survey results will be displayed in Neurology
